How partitioning, collecting and spilling work in MapReduce
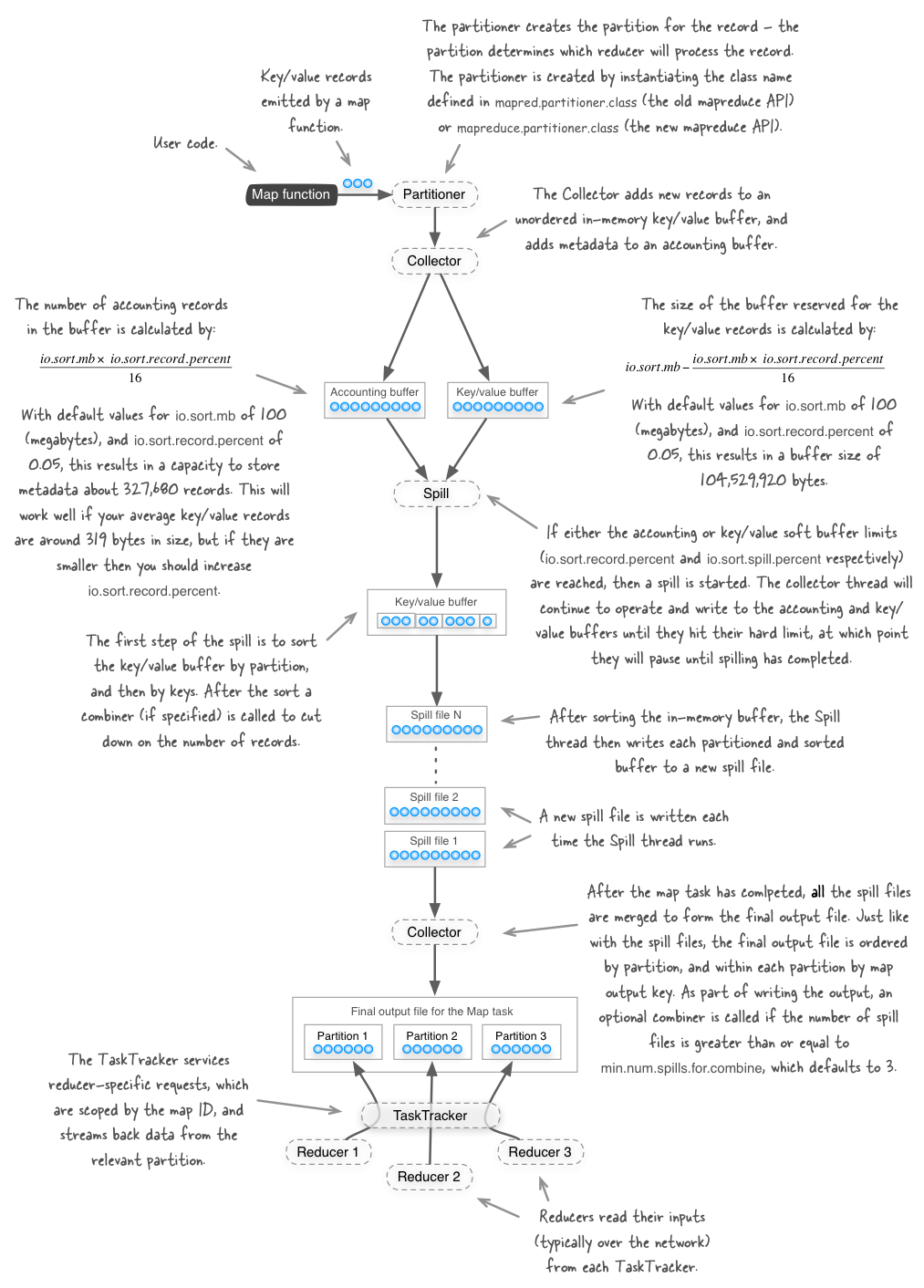
The figure below shows the various steps that the Hadoop MapReduce framework takes after your map function emits a key/value output record. Please note that this figure represents what’s happening with Hadoop versions 1.x and earlier - in Hadoop 2.x there have been some changes which will be discussed in a future blog post.
My book Hadoop in Practice (Manning Publications) in chapter 6 discusses how some of the configuration values in the figure should be tweaked when you start working with mid to large-size Hadoop clusters.
About the author

Alex Holmes works on tough big-data problems. He is a software engineer, author, speaker, and blogger specializing in large-scale Hadoop projects. He is the author of Hadoop in Practice, a book published by Manning Publications. He has presented multiple times at JavaOne, and is a JavaOne Rock Star.
If you want to see what Alex is up to you can check out his work on GitHub, or follow him on Twitter or Google+.
RECENT BLOG POSTS
-
Configuring memory for MapReduce running on YARN
This post examines the various memory configuration settings for your MapReduce job.
-
Big data anti-patterns presentation
Details on the presentation I have at JavaOne in 2015 on big data antipatterns.
-
Understanding how Parquet integrates with Avro, Thrift and Protocol Buffers
Parquet offers integration with a number of object models, and this post shows how Parquet supports various object models.
-
Using Oozie 4.4.0 with Hadoop 2.2
Patching Oozie's build so that you can create a package targetting Hadoop 2.2.0.
-
Hadoop in Practice, Second Edition
A sneak peek at what's coming in the second edition of my book.

